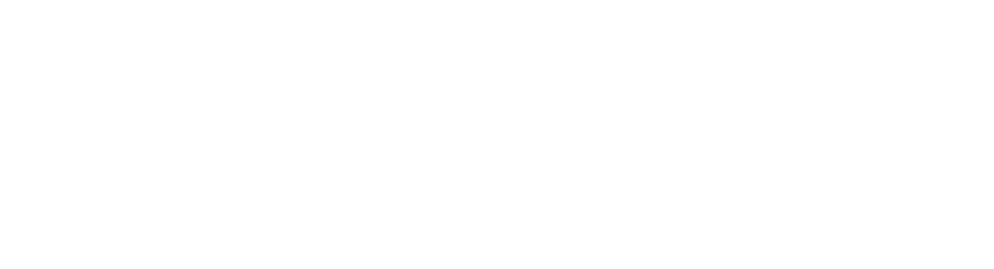Table Of Content
What is ERP Software?
ERP Explained
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning, which manages all key business processes within a single system. These processes include finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain, services, procurement, etc. ERP helps coordinate and optimize these processes using a common database and system of record.
Today's ERP systems are significantly more advanced and distinct from those of the past. They are now cloud-based and utilize the latest technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, to provide intelligent automation, increased efficiency, and real-time insights throughout the business. Modern cloud ERP software also connects internal operations with external partners and networks, allowing companies to collaborate, adapt, and compete in the global market.

Why do businesses need ERP?
ERP software is often called "a business's central nervous system" because it provides the automation, integration, and intelligence for daily operations. ERP also ensures that all business data is consistent and accurate, creating a single source of truth.
ERP is essential for every business function. Finance needs an ERP to close the books more efficiently. Sales require an ERP to manage all customer orders. Logistics requires an ERP to deliver the right products and services on time, and accounts payable needs an ERP to pay suppliers on time and accurately. Management needs ERP to monitor business performance and make informed decisions. Banks and shareholders require an ERP to verify financial records and trust the data and analysis.
The value of ERP software is evident from the increasing demand for it. According to G2, "The global ERP software market is expected to reach US$78.40 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2019 to 2026."
Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is the cohesive force that combines various computer systems within large organizations. Without an ERP application, each department would operate within its own system tailored for specific tasks. However, ERP software unifies these systems under a single application with a unified interface, ensuring seamless accessibility across departments.
What Does ERP Do?
ERP applications facilitate seamless communication and information sharing among different departments within the company. By aggregating data on the activities and statuses of various divisions, ERP makes this information readily available to other parts of the organization, enhancing productivity.
ERP applications contribute to a corporation's self-awareness by integrating information on production, finance, distribution, and human resources. ERP eliminates costly redundancies and incompatible technologies by bridging the different technologies each business segment utilizes. This integration often encompasses accounts payable, stock control systems, order-monitoring systems, and customer databases into one cohesive system.
How Does It Work?
ERP has evolved from traditional software models reliant on physical client servers and manual entry systems to cloud-based software with remote, web-based access. Typically maintained by the creator company, the platform offers services to client companies through rentals.
Businesses select the desired applications, which are loaded onto the server rented by the client's hosting company. Both parties collaborate to integrate the client's processes and data into the platform. Once all departments are linked to the system, data is centralized on the server and instantly accessible to authorized users. Reports featuring metrics, graphs, or other visual aids facilitate the assessment of the business's and its departments' performance.
9 Key Benefits of Enterprise Resource Planning
- Cost Savings: ERP systems offer significant savings by automating repetitive tasks, minimizing errors, and reducing the need for additional hires as the business grows. Additionally, cloud-based ERP solutions often provide incremental value beyond the initial investment.
- Workflow Visibility: Consolidating workflows and information within a single system grants employees instant access to project statuses and performance metrics relevant to their roles.
- Reporting and Analytics: ERP systems offer robust reporting and analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyze data comprehensively.
- Centralized Data: With access to real-time data across the company, ERPs uncover meaningful trends and provide extensive business insights, facilitating informed decision-making by organizational leaders.
- Regulatory Compliance: ERP systems help maintain regulatory compliance by tracking transaction lifecycles, ensuring adherence to approval workflows, and generating financial reports that meet industry standards.
- Risk Management through Mobility: ERP technology enhances risk management by providing granular access control, defined approval workflows, and accurate data, which prevents errors that can lead to lost sales or fines. Real-time visibility enables swift risk mitigation in response to business disruptions.
- Data Security: ERP providers prioritize data security, employing cutting-edge protocols to safeguard critical information from cyber threats. Cloud-based ERP solutions, managed by vendors, offer enhanced security measures to protect against potential attacks.
- Increased Productivity: ERP solutions facilitate information sharing among teams, breaking down departmental barriers and enabling employees to collaborate effectively. By providing real-time access to relevant data, ERPs enhance employee productivity and efficiency.
- Forecasting: Accurate forecasting is vital for finance departments. With ERP systems, organizations can swiftly adjust plans using real-time data. Integration between ERP and planning systems streamlines processes, eliminating the need for manual coordination.
8 Core ERP Modules
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems comprise modules tailored to support specific business processes such as finance, procurement, manufacturing, and more. These modules are integral components within the ERP framework, providing employees with the transactions and insights necessary to perform their roles effectively. Let's delve into the critical elements of an ERP system:
1. Finance: The finance and accounting module is the foundation of most ERP systems. It oversees tasks such as managing the general ledger, automating financial processes, tracking accounts payable and receivable, facilitating efficient book closure, generating financial reports, ensuring compliance with revenue recognition standards, and mitigating financial risks.
2. Human Resources Management: An HR module is standard in most ERP systems, offering core functionalities like time and attendance tracking, payroll management, and employee management. Additionally, add-ons or comprehensive human capital management (HCM) suites can integrate with ERP systems to enhance HR capabilities, including workforce analytics and employee experience management.
3. Supply Chain Management: This module monitors the movement of goods and supplies throughout the supply chain, offering real-time inventory management, warehousing operations, transportation management, and logistics optimization to enhance visibility and resilience.
4. Customer Relationship Management: CRM is a crucial module for businesses across industries, streamlining client communications, lead management, and customer service. It enhances sales efforts and fosters lasting customer relationships.
5. Inventory Management: An inventory management module provides real-time updates on inventory levels, down to the SKU level, and tracks critical inventory metrics. Essential for product-based companies, it optimizes stock levels based on current and projected demand.
6. Enterprise Project Management: Services businesses frequently rely on a professional services automation (PSA) or project management module to plan and monitor projects, including resource allocation and time tracking. This module simplifies client billing and promotes collaboration among project team members.
7. Material Requirement Planning: It offers inventory visibility to meet demand, optimizing stock levels and production schedules. Based on demand and bills of materials (BOMs), the required raw materials, components, and subassemblies are determined to accelerate the production process and assemble finished goods.
8. Management Control: The MC module helps businesses monitor financial performance, budgeting, cost management, and decision-making. It includes financial planning, budgeting, cost analysis, and variance reporting features.
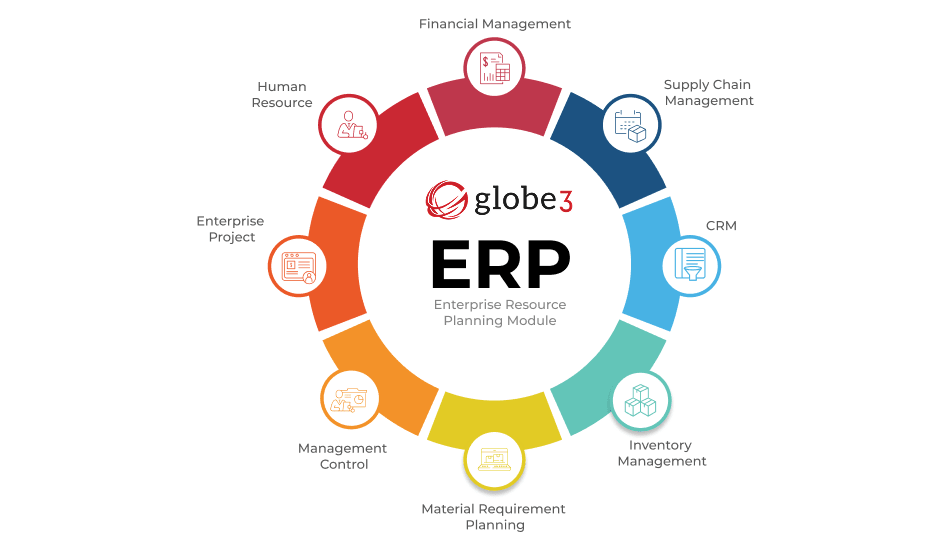
ERP software system types
There are several types of ERP deployment methods available, each offering unique benefits to suit different business needs:
1. Cloud ERP
- Hosted in the cloud and delivered as a subscription service over the Internet.
- The software provider manages maintenance, updates, and security.
- Offers advantages such as lower upfront costs, scalability, agility, and easier integration.
2. On-Premise ERP:
- In the traditional model, the software is installed and managed on-site within your data center.
- Provides complete control over hardware and software but requires internal staff for maintenance and updates.
- Many businesses are transitioning from on-premise to cloud deployments for enhanced scalability and efficiency.
3. Hybrid ERP:
- Combines elements of both cloud and on-premise deployments to meet specific business requirements.
- Some ERP applications and data are hosted in the cloud, while others remain on-premises.
- Also known as two-tier ERP, this model offers flexibility in leveraging cloud benefits while retaining control over certain deployment aspects.
Careful consideration of these ERP deployment options is essential to determine the most suitable approach for your organization's objectives and operational needs.
ERP use cases
Professional services organizations, such as accounting and engineering firms, require highly functional ERP platforms for seamless project collaboration and delivery. Speed and accuracy are crucial to avoid delays that impact billable hours and profitability. Integrated data provides real-time insights across teams.
Wholesalers utilize specialized ERP modules to achieve comprehensive visibility and control over sourcing and inventory levels. Tight coordination across the supply chain through optimized ordering and stock tracking helps reduce costs and maintain service levels.
The construction industry also benefits significantly from ERP implementations. Large contractors and builders utilize integrated solutions to manage projects digitally, facilitating seamless coordination among subcontractors, clients, and suppliers. Real-time visibility into schedules, budgets, procurement, and other key areas helps construction firms avoid costly delays.
Retail operations have undergone rapid evolution in the digital commerce era. Retail ERP powers omnichannel fulfillment and drives personalized engagement. Advanced analytics enhance customer lifetime value by guiding clever marketing, enabling proactive support, and generating actionable insights from digital touchpoints. Continuous improvements to the buying experience and last-mile delivery strengthen customer relationships and loyalty over time.
Enhancing Business Operations with ERP Integration
Today's ERP systems are powerhouses of business functionality; however, their full potential is unlocked when they seamlessly integrate with other vital applications and data sources. This includes CRM and HCM software, e-commerce platforms, specialized industry solutions, and other ERP systems. Through ERP integration, businesses can achieve a cohesive view of disparate information systems, bolstering process efficiency, enriching customer experiences, and fostering collaboration among teams and external partners.
Modern ERPs are designed for openness and adaptability, enabling seamless integration with a wide range of software products. This is achieved through connectors or bespoke adapters, such as application programming interfaces (APIs). Alternative integration methods include ESBs (Enterprise Service Buses) and iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service), with the latter being a favored cloud-based solution for contemporary enterprises. iPaaS platforms enable swift synchronization of on-premise or cloud-based ERPs with SaaS applications from the same provider or third-party vendors. Their appeal lies in minimal coding requirements, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. They offer additional functionalities such as automated API creation, machine learning-enhanced data integration, IoT network integration, and access to prebuilt content.
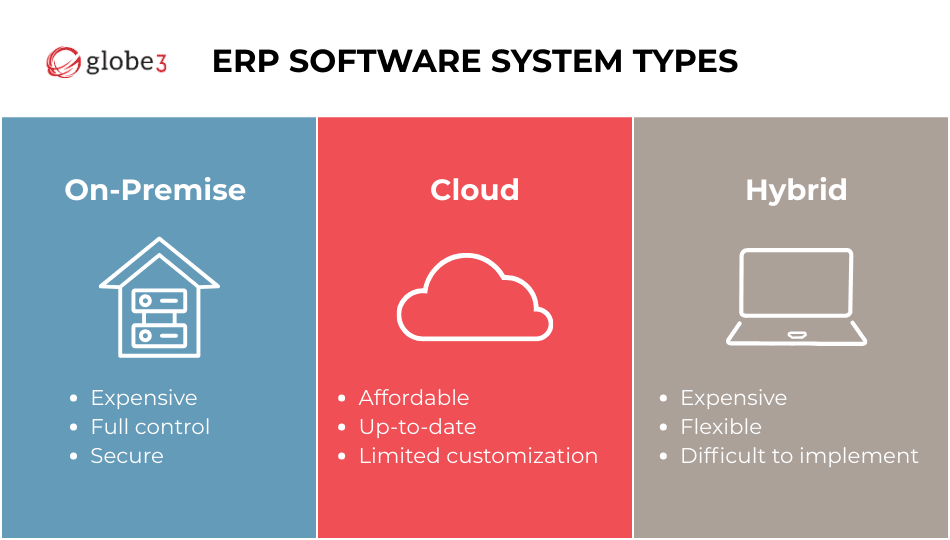
Understanding the Implications of the Cost of ERP
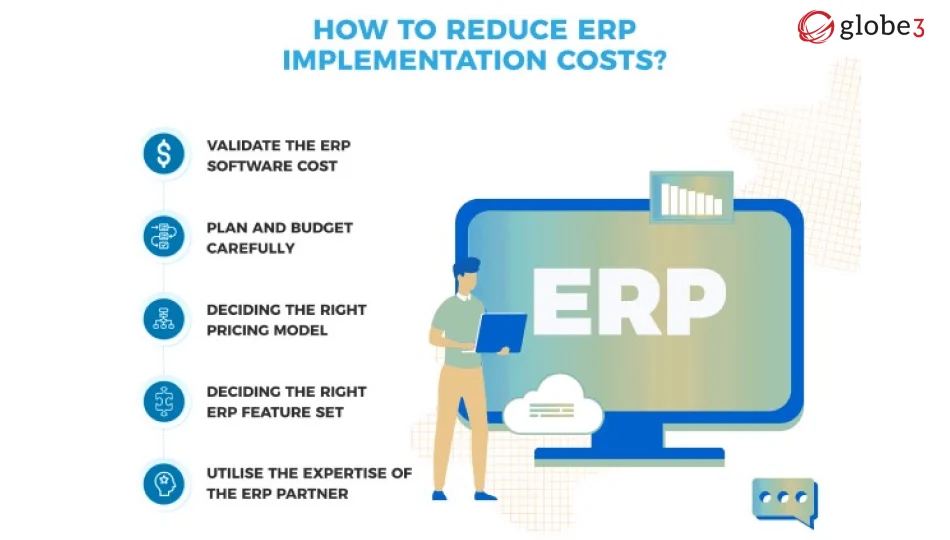
Factors such as vendor choice, selected modules, and the deployment method influence the investment in an ERP system. Typically, cloud-based ERPs are more economical than on-premise systems, as they eliminate the need for hardware investments and specialized IT personnel. The vendor manages maintenance, charging a subscription fee, often user-based, on an annual or monthly basis.
When assessing the ROI and TCO of a new ERP implementation, it's crucial to consider both the initial software and deployment expenses, as well as the ongoing workforce costs. Cloud and hybrid models introduce new variables, including software maintenance, infrastructure, computing capacity, downtime, recovery procedures, security, privacy, and IT staffing expenses. Cloud solutions effectively reduce capital and operational expenditures, enhancing ROI and TCO.
7 Key Incentives for Transitioning to a Cloud-Based ERP Solution
The transition to a cloud-based system may take time, but the reluctance to embrace the cloud's advantages is no longer viable. Here are seven compelling reasons to consider cloud applications as a replacement or enhancement to your existing on-premises systems:
1. Embrace Cutting-Edge SaaS Innovations: Cloud-based systems are at the forefront of adopting next-generation technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), which continuously enhance system capabilities without requiring manual updates.
2. Enhance Your Current ERP System: Integrating cloud applications with your existing ERP can revitalize and extend its functionality, allowing you to leverage cloud technology without overhauling your current system.
3. Leverage Modern Technologies: Cloud applications that align with your existing ERP modules enable you to benefit from the latest technological advancements and user experiences, adding value to your business operations without disruptive changes.
4. Minimize Reliance on Third Parties: Cloud applications linked to your ERP can generate business intelligence internally, reducing the need for third-party vendors and streamlining your analytics processes.
5. Modernize Financial Operations: Unlike legacy systems, cloud-based technologies are designed with modern reporting and operational requirements in mind, offering a more effective platform for ERP solutions.
6. Access Superior Security Measures: Cloud service providers invest heavily in security, with dedicated teams monitoring and addressing security concerns around the clock.
7. Draw Top Talent: New professionals expect intuitive, mobile, and always-accessible technology. Companies that need to update their systems may require assistance in attracting the best candidates.
By considering these factors, businesses can make informed decisions about their ERP strategies and stay competitive in an increasingly cloud-oriented world.
Top 10 Essential Features to Consider When Choosing an ERP Solution
When selecting an ERP system, it's crucial to consider these ten key features that can significantly enhance your business operations:
- Integration: A seamless connection of all business processes to eliminate data silos and improve efficiency.
- Automation: The capability to automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and free up staff for higher-value work.
- Data Analysis: Robust data analysis tools that transform data into actionable insights for optimizing operations and identifying new opportunities.
- Reporting: Comprehensive reporting features for accurate financial management and operational insights.
- Financial Management: Core accounting functions like general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, and payroll management.
- Customer Relationship Management: Tools to manage customer data, improve interactions, and drive sales.
- Sales & Marketing: Features that support sales processes and marketing campaigns to boost revenue.
- Human Resource Management: Management of employee data, payroll, benefits, and recruitment processes.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimization of inventory, order, and supply chain processes for increased efficiency.
- Manufacturing: Integration of production, procurement, and distribution to streamline manufacturing operations. These features are foundational to a robust ERP system that can adapt to your business's unique needs, providing a competitive edge in today's fast-paced market.
Get started with Globe3 ERP

Embark on a journey with Globe3's ERP Cloud and discover how it transforms the complex landscape of traditional ERP systems. By integrating cutting-edge cloud services, Globe3 ERP Cloud synchronizes your teams, consolidates data, and offers instant insights, empowering your finance team to make informed decisions. As a cloud-based service, it equips your organization to stay ahead of the curve and adapt swiftly to change.
The SaaS model of Globe3 ensures that your software remains current, incorporating the freshest features, functions, and industry best practices. Globe3's commitment to regular updates ensures that subscribers receive the benefits of groundbreaking technologies, including AI, digital assistants, machine learning, blockchain, augmented reality, and IoT, at a consistent pace.
Leveraging these advancements, your organization can refine its best practices as the ERP software evolves. Processes that once demanded extensive manual effort, such as financial reconciliation, can now be automated. Moreover, the ERP system provides a thorough, instantaneous view of all business operations, from the front office to the warehouse and production lines, accessible to relevant personnel on their mobile devices.
Globe3's ERP Cloud is crafted for the digital era, embracing mobility, social connectivity, analytics, and the forefront of technological innovation. Settling for anything less risks leaving your organization behind in an ever-progressing world.
Let's explore the Full Capabilities of Globe3 ERP Software - Best ERP Solutions for Small and Medium Enterprises Based in Singapore.
Contact Us Now for a Free Consultation!
ISO 27001 Certification: A Milestone in TNO Systems’ Commitment to Information Security
TNO Systems Pte Ltd is proud to announce that it has successfully achieved ISO 27001 certification, a globally recognized Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) standard.
Top 6 Benefits That Accounting Software Brings To Your Business
Feeling worn out from manually tracking financial transactions in bookkeeping and needing help to stay ahead of the numbers? Look into accounting software, the modern solution that can transform your
Best Payroll Systems for SMEs in Singapore Systems
Managing payroll is crucial for SMEs in Singapore. It involves processing employee salaries and benefits and ensuring compliance with regulations. Effective payroll management builds employee trust